- ELECTRICAL NEWS
- 1 likes
- 4220 views
- 0 comments

Characteristics of Electrical Cables | Complete Guide
The world of electrical cables is more complex than you might think. Not everyone is aware of the existence of a wide range of cable types, each suitable for a specific use.
A Guide to the Most Used Electrical Cables
In this guide, we will focus on the most commonly used and easily available electrical cables on the market.
New Regulations and the Future of Electrical Cables: The CPR Regulation
The recent CPR regulation (construction products regulation) has defined new directives for the production of cables. This has led to significant changes in the electrical cable industry. Many of the cables that we used to see in the last 20 years have disappeared or will disappear soon.
Electrical cables and fire resistance: a guide to interpreting the acronyms
Do you often wonder what the acronym printed on electrical cables regarding their fire resistance means? It is important to know it, as it indicates the classification of cables based on this particular characteristic. The acronym you find, for example, Cca-s3,d1,a3, refers precisely to this.
What does the acronym indicate about the fire resistance of electrical cables?
Before going into detail, it is useful to know that cables are divided into seven classes, depending on the results highlighted in the resistance tests. This classification criterion is regulated by the EN50399 Standard, which deals with common test methods and measurement of heat emission and smoke production on cables during the flame development test.
The highest class of cables with respect to fire resistance is Aca, while the lowest is Fca. But these are not the only elements to take into account.
The additional acronyms on electrical cables: what do they indicate?
In addition to the main classification, there are other acronyms on the cable that indicate specific characteristics. In particular, these letters distinguish:
- The letter 'a', which indicates corrosivity, varying from a1 to a3
- The letter 's', which symbolizes the opacity of the smoke, varying from s1 to s3
- The letter 'd', which concerns the dripping of rubber in case of fire, varying from d0 to d2
Here's how to decipher the acronym Cca-s3,d1,a3: it symbolizes the fire resistance class of the electric cable (Cca), the opacity of the fumes (s3), the dripping of the rubber (d1) and the corrosivity (a3).
Understand the names of electrical cables
The name assigned to electrical cables is not causal, but is always indicative of their specific characteristics. This is why it is important to know how to correctly interpret the names of the cables.
Specific features highlighted by cable naming
All electrical cables have a specific name that reveals their particular characteristics, helping the user to identify the type of cable best suited to their needs.
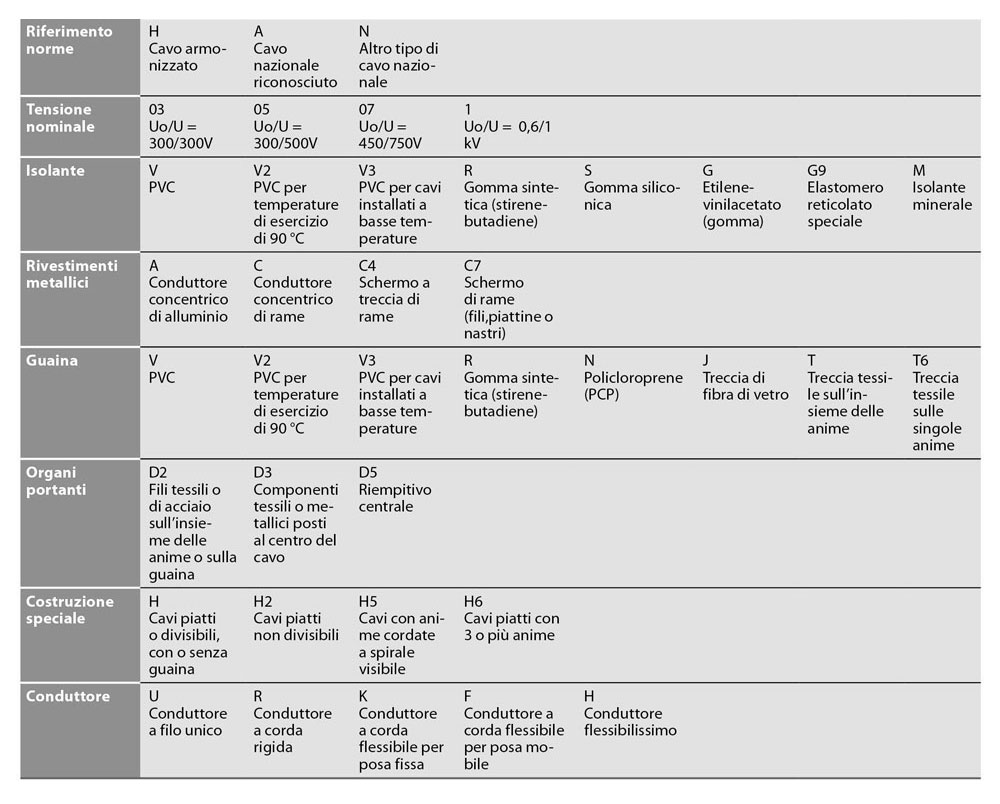
Summary table: groups of designation, denomination and symbol
To make it easier to understand the different characteristics indicated by the cable names, here is a summary table that includes the different designation groups, the relative name and the respective symbol.
Guide to the capacity of electrical cables: variables to consider
We know well that the choice of the section of an electrical cable is not a simple and direct calculation as various variables come into play, making the formula not consistently mathematical. The variables to consider concern both civil and industrial systems and refer to a series of factors.
What factors should you consider when selecting electrical cables?
First of all, to correctly choose the electrical cable based on wattage absorption, it is important to evaluate these factors:
- The user's voltage, therefore whether the current is single-phase or three-phase
- The distance between the power supply and the user
- Whether the current is direct or alternating.
Determine the section of the electrical cable based on the variables
Considering this information, you will be able to calculate the cable cross-section. For example, if you want to connect a 2KW oven to a socket 30cm away, it is convenient to use a 2.5mm2 cable.
On the contrary, imagine that the same oven is 600 meters away: in that case you will need a 25mm2 cable. It is essential to consider the voltage drop, which according to the CEI 64.8 standard (art. 525), should not exceed 4%.







Comments (0)